|
|
|
Raster Modeling and Analysis
created by:
Idung Risdiyanto
MIT Student/99731
INTRODUCTION
Advance
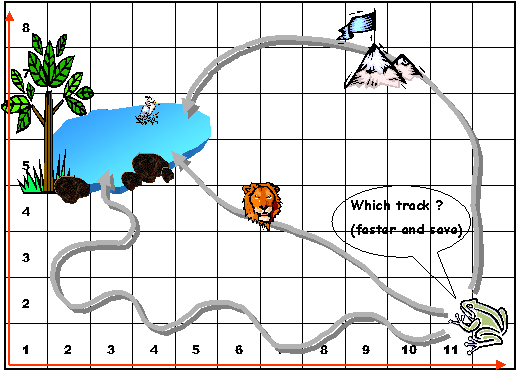
GIS Assignment #3 has the title raster modeling and analysis.
It’s main how to create the raster modeling and analysis to solve the
GIS problem. Generally, raster modeling is the model based on raster data,
it’s main used the grid data that each of cell contained the information such
as elevation, rain intensity etc and make the manipulated this data.
Using cell information we can make the analysis a object or lanscape on
the surface depend on our objectives. .
For this assignment the problem will be try to apply the raster modeling
for watershed including the analysis.
Watershed
can define by the area contained one or more river or stream and to be around by
boundaries as topography or elevation. According Gibeau (2000), watershed define
by the total area flowing to a given outlet, or pour point.
Watershed also called with the other common such as river basin,
catchment area or contributing area. Many
study have been done about watershed including geographical information system.
We could say that a watershed provides a powerfull study and
management unit, because watershed is defined by natural hydrology, represent
the most logical basis for managing water resources.
Many source provide by watershed and many procedures for exploration,
exploitation and manage there. So,
in this assignment we will use the watershed as object study.
Otherwise, the watershed is the unique area can be analysis and the good
object to learn raster modeling.
Actually,
the watershed area often presented using maps or analog data.
Some times, a watershed provided by different map scales and criteria.
This fact, can make the user will be confused. Now, with the computer hardware and software, we can create
the information about watershed into GIS based on computer or digital system.
GIS technology based on computer are useful in digital form and at a wide range
of map scales and data from the largest available scale are preferable for the
finest resolution.
Other
object to understanding raster modeling and analysis is least cost analysis.
Actually, these are procedure to get the information when we have project
planning and we want to use the nformation in order to our project more
efficient or high benefit and low cost. For
example, when we plant to develop the irrigation area, we can use GIS technology
for analyzing and extracted the information in order we can know where the water
Dam or irrigation network will be build with the low cost. To calculated the cost, we should consider about unit and
procedures will be used.
Consider above explanation, these assignments have two main work or task; raster modeling and analysis for watershed and second one is cost-benefit analysis. To creation of the task, we should learn about map algebra (local, focal, zonal and global request). Understanding about map algebra will be help to make easier when we create the raster modeling and analysis. Otherwise, some method will be used in this assignment and we should make the comparison between results of the methods. In this assignment we will focus on ArcView Spatial Analysis to create the task assignment.
BACKGROUND THEORY
Background theory will be explained about watershed, map algebra and least cost analysis. In the each of path also explained how to creation and operate it. This is necessary to explained because before we created the task assignment we need to learn the theory about object study (watershed) and the theory of raster analysis.
Watershed
The terminology of watershed is the total area flowing to a given outlet, or
pour point. Out let or pour point
is the point at which water flow out of an sea or other water body and lowest
point along the boundary of the watershed.
Somewhere the area often has one or more watershed and between watersheds
have the boundary or drainage divide. In hydrology, the watershed area should be content one or
more sub-watershed. It define by
the total area flowing to a given outlet by one stream or river.
To more clearly we can see Figure 1.
According Gibeau (2000), Using
the watershed concept, one can start with study of any number of small sub
systems (e.g., a particular marsh or sub-watershed; or a particular pollutant,
such as salt), and continually relate these small-scale issues to questions of
larger-scale watershed system health.
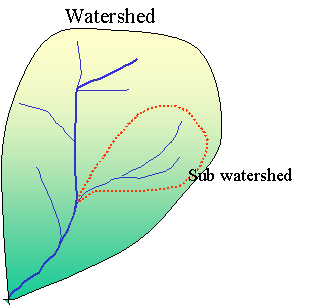
Figure 1. Illustration of watershed and sub-watershed
Watershed data have the potential uses, for example for assessment of impacts of increasing urbanization on the water quality of a major rivers, boundaries (ridges) and drainage lines (streams) can be used to help identify suitable wildlife corridors and water supply for urban area and agriculture.
The problem that often found when we will manage the watershed is where there and how to make the boundaries of watershed. Otherwise, may be causing by the map or data about it not available. Now, using GIS assignment we can determination the area of watershed using the independent contour data and independent river network data. Independent data its main the watershed area will be creating only use the contour data or river network data. To created we used the digital elevation model (DEM).
When we created the watershed using DEM data we must consider about the area that blank or no data and how to solve this problem. Generally, the steps of creating watershed can be divided two section; using DEM data and burning stream digitized. Steps of watershed creating using DEM have many steps; sink filling, flow direction, flow accumulation, identifying stream cell, labeling the link and determining the watershed or sub watershed area.
Creating
watershed based on depressionless DEM
Sink
filling
Sink filling is the technique hot to make the DEM data free from sink or
the DEM must a depression less DEM. This
is a desired input to create watershed or models of flow each of cell on the
surface. This is very necessary to
consider, because the accurate of watershed creation to be determination by sink
filling product.
Flow direction is one of hydrologic characteristic about the flow from
every cell on the surface grid. This
is done with the FlowDirection request. The
valid flow direction will be getting, if the sink filling as input is right.
Flow directions have eight directions and each of direction have the
specific number such as Figure 2.
|
32 |
64 |
128 |
|
16 |
X |
1 |
|
8 |
4 |
2 |
Figure
2. Flow direction assign number
The
number of flow direction determine by finding the direction of the steepest
descent, or maximum drop, for each cell. This
is calculated by the following :
Maximum drop = change in z value/distance
Where
the distance is determined between cell centers.
Flow accumulation
Flow accumulation is accumulated weight of all cells flowing into each downslope cell in the output grid. If no weight grid is provided, a weight of one is applied to each cell, and the value of cells in the output grid will be the number of cells that flow into each cell. The weight grid might be used to determine how much rain might run out os a given watershed.
Its main how to know the stream network. Refer from flow accumulation, the stream network will be provided by information each cell. The area with the cell contained information about flow accumulation is the requirement when will be created stream network.
Labeling the Links
Labeling
the links is assign unique values to sections of raster linear network between
intersections. Labeling the link
will be created if identifying stream cells have been get the result.
The input must be a raster linear network.
Its should be represented as values greater than or equal to one a
background of No Data.
A
watershed is an area that drains water and other substances to a common outlet
as concentrated drainage. Other common terms for a watershed are: basin,
catchment , or contributing area. This area is normally defined as the total
area flowing to a given outlet, or pour point. The boundary between two
watersheds is referred to as a watershed boundary or drainage divide.
An outlet, or pour point is the point at which water flows out of an
area. This is the lowest point along the boundary of the watershed. The cells in
the source Grid are used as pour points above which the contributing area is
determined. Source cells may be features such as dams or stream gauges, for
which determine characteristics of the contributing area.
Creating
watershed based on burning stream into a DEM
Burning stream data into DEM have the objective how to create watershed based on river (line dataset) on the DEM surface. Burning stream consist of raising the levation of all the cells but those that coincide with the digitized streams. The assume, water is forced to remain in the stream once it gets there.
Map
algebra for spatial analysis
Map
algebra is the specific languages that design for geographic cell-based system.
Some software such as ArcInfo and ArcView use map algebra to perform
analysis on grids. We can called
the map algebra is grid language takes advantages of mathematical operators and
spatial function. Use it, will be
allow the operator to create simple and complex expressions become easier.
In arcView, map algebra often applied into map calculator or avenue
script.
Map
algebra will Establishes a set of conventions for data-processing control and
the conventions describing how operations
are specified, Data to operate on and Order in which the operations should be
processed.
For
spatial analysis we must consider about four categories based on the amount of
information (level) that is used to compute the value at each cell in the output
grid. The four categories are :
-
Local request
: work on single cells
-
Focal request :
work on cells within a neighbourhood
Zonal request : work on cells within zones
Global request : work on all cells in a grid (global functions)
This
is a Local functions perform
cell-by-cell processing. The
specific is the Output value at each location is only dependent on the input
cell at that location and the value
of the single cell, regardless of the values of its neighbors, has a direct
influence on the value of the output. The
following categories including in the focal request are;Trigonometric,
Exponential, Logarithmic, Reclassification and Statistical.
Figure 3 as shown the illustration of local request.
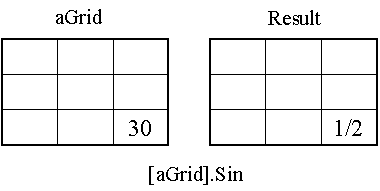
Figure
3. The illustration of focal
request
The value at each cell in the output Grid depends on the value of a specified neighborhood of cells in the input Grids. A neighborhood configuration determines which cells surrounding the processing cell should be used in the calculation of each output value. The illustration of focal request can be seen in Figure 4.
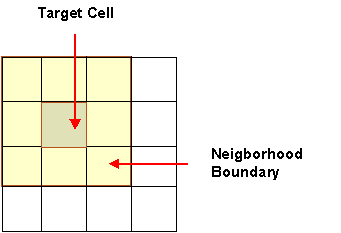
Figure
4. The illustration of focal
request
Zonal request used to perform
operations on a zone-by-zone basis. The
process is computing a single output value for each zone in the input grid. Once the statistic is calculated for a zone, that single
value is written to every cell in the zone.
Zones could be land use types,
forest zones, buffer zones, etc and a region is a group of connected cells with
the same value.
Similar
to local functions except that the neighborhood in a zonal function is the
configurations of the zones or features of the input zone grid, not a specified
neighborhood shape. This request
has 2 categories for map algebra:
-
Statistical
-
Geometrical
This figure is illustration one of all zonal request type.
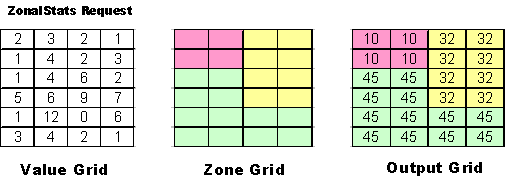
Figure
5. illustration one of all zonal
request type.
Global request is global
calculations require the entire grid as a surface to return the solution.
Surface functions, such as aspect, hillshading and some interpolation
methods are also global requests. Value
at each cell in the output Grid potentially depends on all cells in input Grids.
Least-Cost
Analysis
Actually,
least cost analysis is the procedure to get the information when we have project
planning and we want to use the information in order to our project more
efficient or high benefit and low cost. For
example, when we plant to develop the irrigation area, we can use GIS technology
for analyzing and extracted the information in order we can know where the water
Dam or irrigation network will be build with the low cost.
To calculate the cost, we should consider about unit and procedures will
be used.
To
create the least cost analysis we must consider bout this steps:
1.Determine
a problem/scenario
2.Generate
a cost grid
•
Polygon-grid conversion
•
Reclassification
•
Assign weights and cost surface
•
Create source and destination points
3.Generate
a Cost Distance Grid
4.Generate
Cost Paths
This figure is the illustration for cost path analysis.

Figure 6. The illustration for cost path analysis.
For procedures, result, discussion and conclusion please contact us (200$)